As technology evolves, the choices for enterprise connectivity continue to expand. Two options that are currently making waves are Wi-Fi 6 and 5G. Both offer high throughput and reliability, low latency, and better quality of experience. However, use cases for each can be exclusive, and there can be some crossover as well. So, how do enterprises make the right choice?

In this blog, we will provide guidelines and articulate the differences between these two technologies to help enterprises make informed decisions. We will discuss the salient features of each and where each technology can be most beneficial.
Salient Points of Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 offers a robust eco-system with medium to low-cost end devices and sensors to address connected systems and medium-density IoT. There is a large vendor ecosystem to choose from, with over 43 active chipset vendors and variants available, depending on the application. Attractive price points are available, with chipsets and SoCs available around the $3 price range.
Due to its large permeance, middleware, applications, protocols have all been standardized and deployed in scale. Large enterprises have deployed Identity, policy, device management, intercept systems, and such to be able to manage IT infrastructure effectively. A trained resource pool is available to deploy and troubleshoot Wi-Fi networks. Tools are also available for surveying floor maps and suggesting positioning of access points.
Wi-Fi 6 provides robust security measures built in for user access (802.1X for user and device access) and to secure data (WPA3). It is optimized for capacity (1024 QAM, UL Multiuser MIMO, and DL MIMO are a few examples that enable this). Even though Wi-Fi 6 operates in license-exempt band including 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, techniques are available, and built-in access points to avoid interferences and do channel shifts. AI/ML and location analytics are making great strides in Wi-Fi and have evolved over years to provide deep and meaningful insights to operation teams over the performance of Wi-Fi networks. VoWi-Fi & OpenRoaming have made Wi-Fi a ubiquitous choice of technology for service providers to deploy networks in venues and coverage restrained areas.
Salient Points of 5G
5G is optimized for coverage and capacity, with flexibility to deploy in multiple frequency bands, 256QAM modulation, and offering the flexibility of different frame formats. It offers dedicated spectrum for the enterprise, offering remarkably high reliability for mission-critical applications along with extremely low latency (up to 1ms), enabling priority traffic routing for industrial control systems. It enables seamless handover, consistent QoS, and business automation prospects that were previously unavailable to the enterprise.
The promise of enterprise 5G includes mmTC that can change the landscape of the sensor eco-systems in any industry with a target to offer up to 1M devices per sq.km. 5G offers a comprehensive security umbrella, right from the end devices to the transport and core network elements. Common policy, authorization, and segmentation between the 5G and the enterprise networks are also available and evolving to address the need of the hour. CAPEX and OPEX considerations of deploying such private radio access equipment, core network components, and backhaul connectivity will have to be taken into account as well. Private 5G networks also require specialized skills and expertise to design, deploy, and manage, needing IT / OT administrators to skill up.
Key decision points in a nutshell
Enterprises do not have to choose between these complimentary access technologies. There are, however certain industry verticals and use cases where one of these access technologies becomes a primary choice.
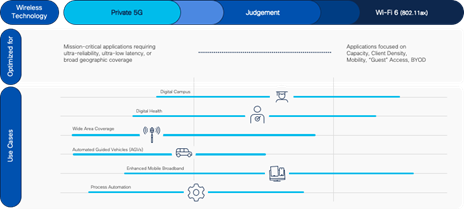
- Heavy Manufacturing, Warehouse / Logistics, Oil & Gas, Alternative Energy, and industries evolving to an Industry 4.0 are the typical target segments for enterprise 5G.
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), AR/VR, high bandwidth video, AGRs, AGVs, Process automation, factory floor reconfiguration, TSN are some examples of use cases driving p5G adoption.
- The explosion of IoT, including Industrial and manufacturing is also seen to be fueling this demand.
- Campus networks with requirements of medium to low device density, backward compatibility, cost, and simpler technology adoption are factors driving the Wi-Fi deployments.
- Education, Healthcare, and other manufacturing verticals are key verticals continuing the Wi-Fi adoption & growth.
Factors such as use cases, availability of private spectrum, device capability & density, mobility of end devices, throughput requirements on the uplink, down link, RoI, and available skillsets will need to be evaluated on a per enterprise basis and a suitable solution of potentially a multi-access technology will need to be arrived at.
A three-year view of network growth, technology adoption, investment protection, and other factors will also play a critical role in this decision making.
Most enterprises currently have a mix of different access technologies, including Wi-Fi 6 & enterprise 5G addressing specific needs. An informed judgement will have to be taken to arrive at a path of eventual migration to enterprise 5G as per the need of the enterprise. Cisco assists enterprises in different stages of this technology journey (Wi-Fi6, Wi-Fi7, pLTE, p5G) and offers end-to-end solutions to address all the needs of the enterprise.